Tarbela reservoir monitoring using remote sensing
LCWU - Lahore, Pakistan - PHC Peridot grant
2023-12-12
I - General presentation: location
Location
- Extent: 120 km2 – Volume: 11.62 Gm3
- Upstream watershed: 208240 km2 (≈ 25 % of the Indus basin) – Hydrological network length: 46115 km
I - General presentation: the reservoir
The Tarbela dam
- Years of construction: 1970 - 1974
- Dam height (thalweg): 148 m
- Dam length: ≈ 2.7 km
- Purpose :
- hydro power: 234 MW, 30 % of the needs of Pakistan
- irrigation: 50 % of total irrigation release
- flood mitigation

Water flowing from the Tarbela dam
I - General presentation: history
Reservoir filling
Totally filled from September 1975
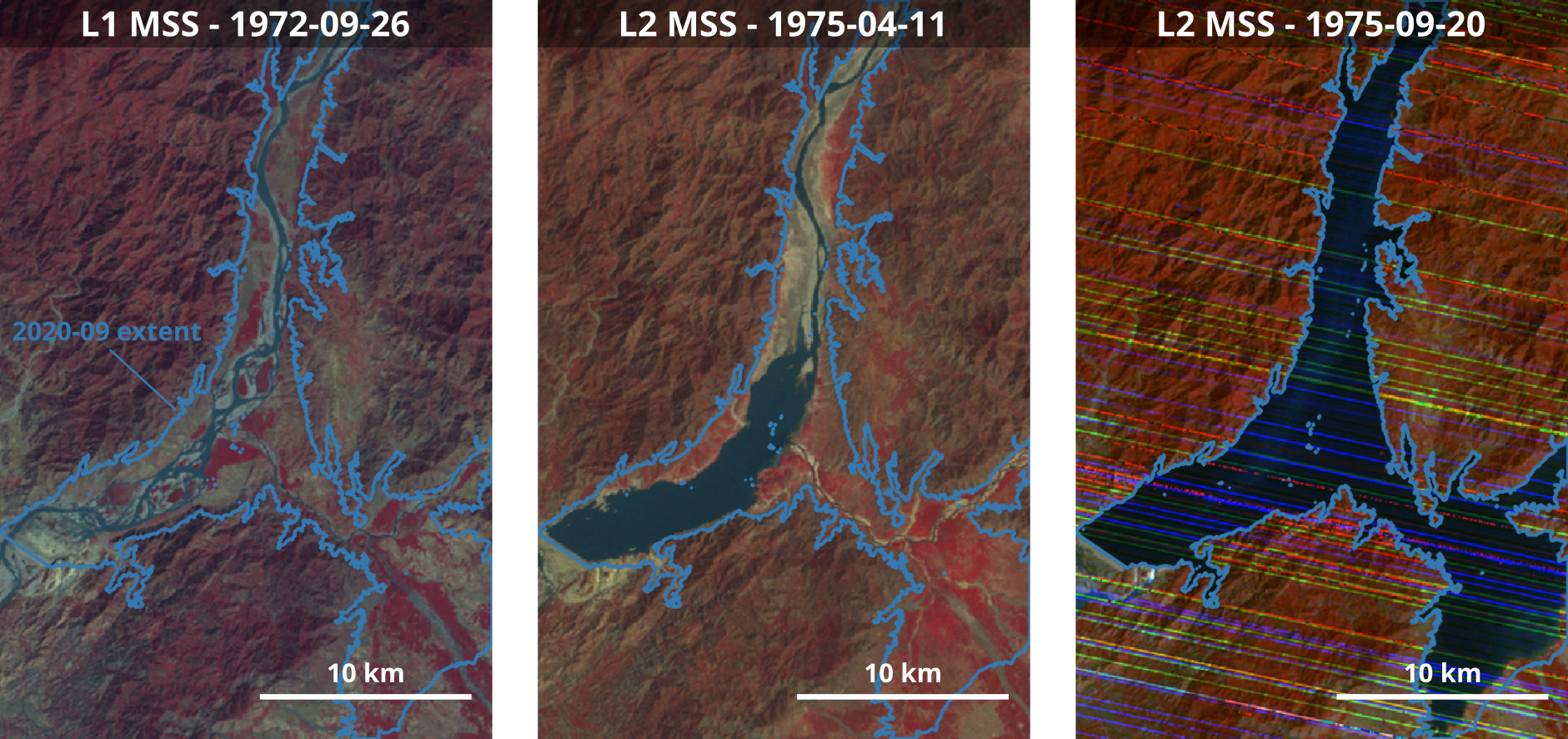
Landsat MSS false color comosites (NIR-R-G) during the filling of the reservoir
II - The issues: sedimentation
High rates of sedimentation
The reservoir has lost 30 % of its storage capacity and 15% of its power generation potential due to sedimentation (Mazhar, Mirza, Butt, et al. (2021))
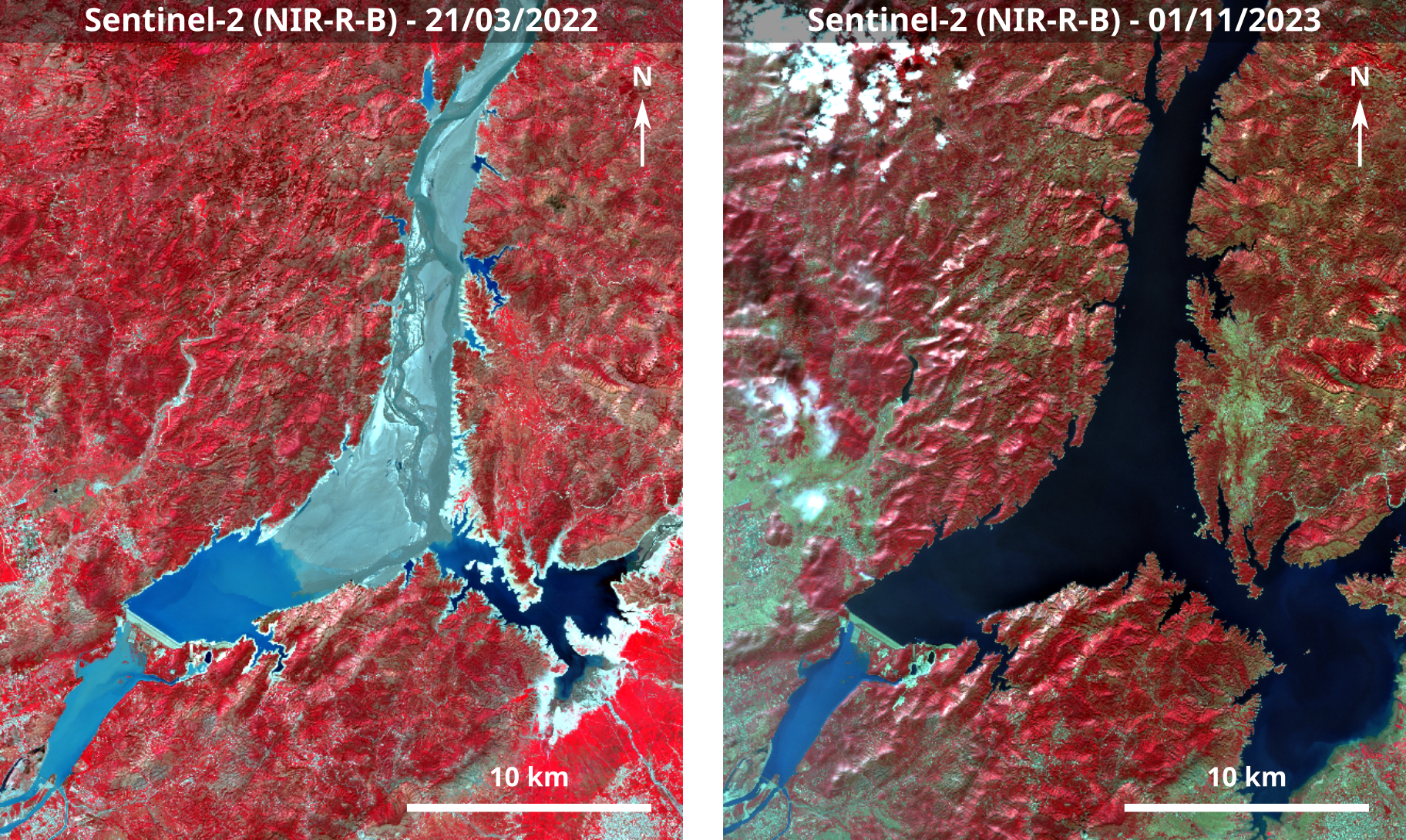

Sentinel-2 colour composites at two different dates.
II - The issues: questions
Scientific questions
- Is it possible to detect any tends in terms of water extent of the Tarbela reservoir through time?
- Is it possible to detect any tends in terms of water quality of the Tarbela reservoir through time?
- What are the links between these trends and the dynamics of the upstream watershed?
Hypothesis
- Remote sensing may help to detect the hydrological annual and pluri-annual hydrological trends
- The trends are linked to dynamics in terms of land use or climatic changes occurring within the upstream basin
III - Data: the Sentinel program
The Sentinel program
6 different missions maintained by the ESA
The Sentinel missions.
III - Data: Sentinel-2
The Sentinel 2 constellation
Two satellites and soon three satellites
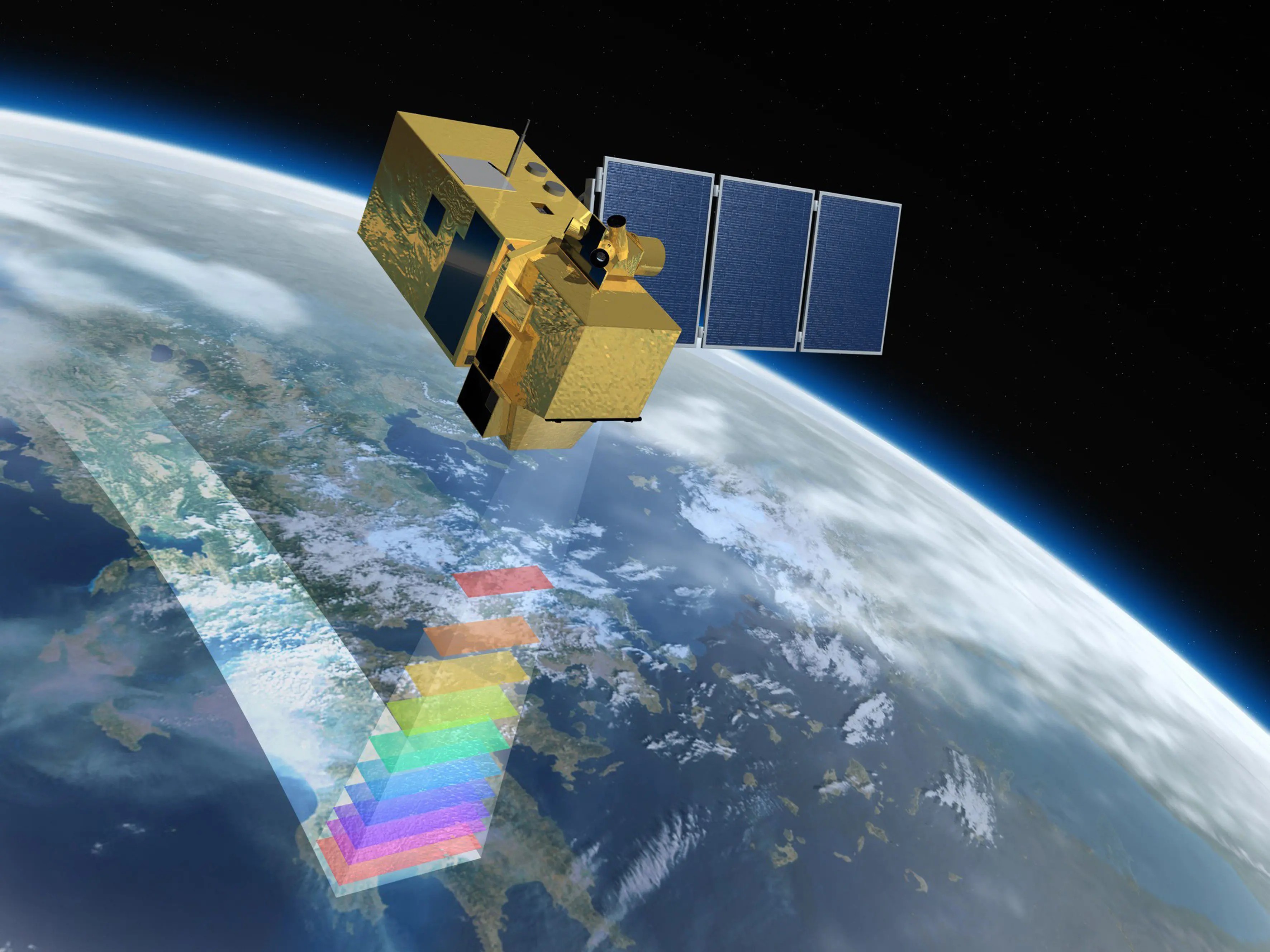

MSI sensor: 13 spectral bands
| Band | Domain | Central l (nm) | Bandwidth(nm) | Resolution (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Coastal | 442.2 | 21 | 60 |
| 02 | Blue | 492.1 | 66 | 10 |
| 03 | Green | 559.0 | 36 | 10 |
| 04 | Red | 664.9 | 31 | 10 |
| 05 | Red Edge 1 | 703.8 | 16 | 20 |
| 06 | Red Edge 2 | 739.1 | 15 | 20 |
| 07 | Red Edge 3 | 779.7 | 20 | 20 |
| 08 | NIR | 832.9 | 106 | 10 |
| 8A | Narrow NIR | 864.0 | 22 | 20 |
| 09 | Water vapour | 943.2 | 21 | 60 |
| 10 | SWIR Cirrus | 1376.9 | 30 | 60 |
| 11 | SWIR 1 | 1610.4 | 94 | 20 |
| 12 | SWIR 2 | 2185.7 | 185 | 20 |
- Sentinel-2A: 10 days
- Sentinel-2B: 10 days
- Sentinel-2A and 2B together: 5 days
| Date | Satellite |
|---|---|
| 2023-10-02 | Sentinel-2A |
| 2023-10-07 | Sentinel-2B |
| 2023-10-12 | Sentinel-2A |
| 2023-10-17 | Sentinel-2B |
| 2023-10-22 | Sentinel-2A |
| 2023-10-27 | Sentinel-2B |
| 2023-11-01 | Sentinel-2A |
| 2023-11-06 | Sentinel-2B |
| 2023-11-11 | Sentinel-2A |
| 2023-11-16 | Sentinel-2B |
| 2023-11-21 | Sentinel-2A |
- L1C: TOA reflectance
- L2A: Surface reflectance processed using the SEN2COR algorithm
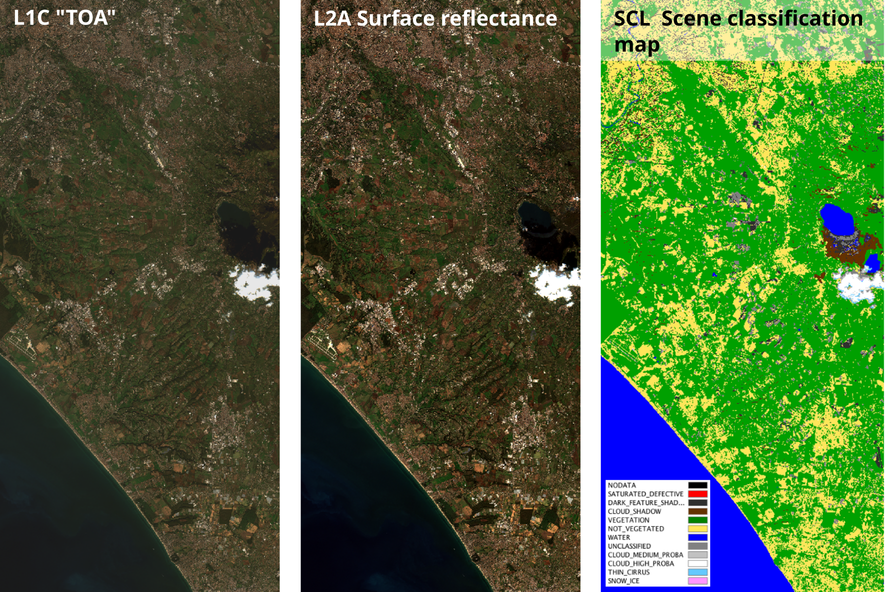
IV - Methods: COG
Data access
Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF: “A Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF (COG) is a regular GeoTIFF file, aimed at being hosted on a HTTP file server, with an internal organization that enables more efficient workflows on the cloud. It does this by leveraging the ability of clients issuing HTTP GET range requests to ask for just the parts of a file they need.”
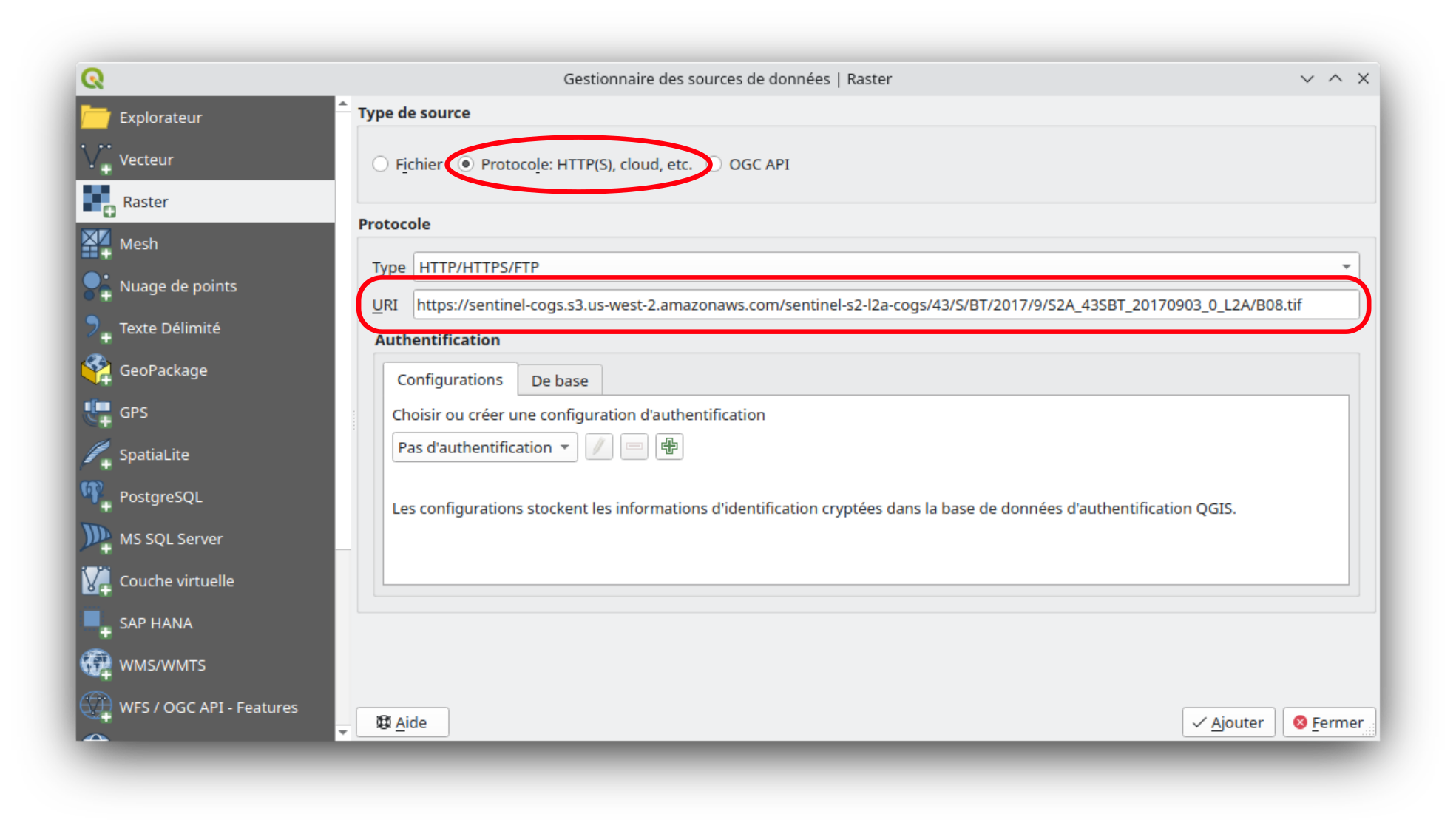
COG in QGIS.
IV - Methods: clouds
Clouds survey
Calculation of clouds proportion only on the study area
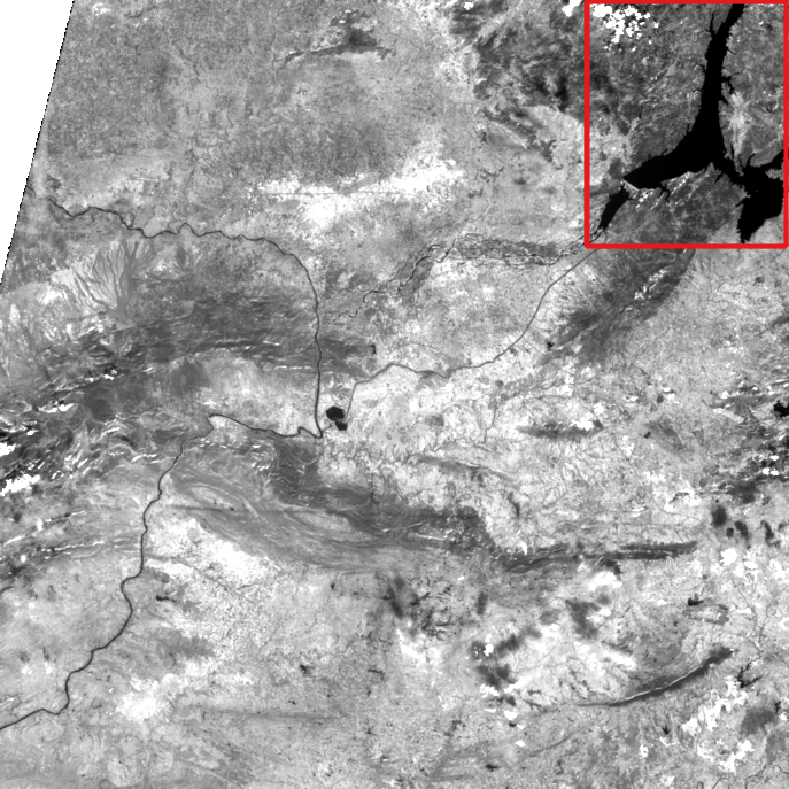

Sentinel-2 tile T43SBT and the study area (red).
Cloud cover over the whole tile (as provided in the metadata of the image): 15 %
IV - Methods
Clouds survey
Calculation of clouds proportion only on the study area
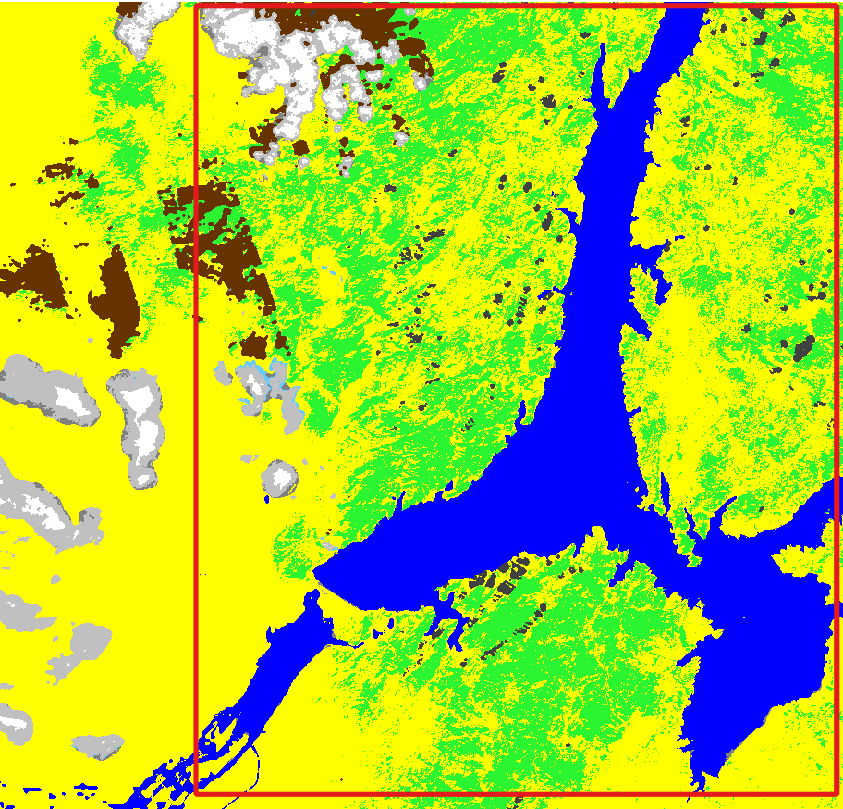
SCL raster for the study area
Cloud cover over the study area (as calculated using the SCL raster): 9 %
IV - Methods: clouds chronics
Chronics of cloud cover
Cloud cover the study area for the whole chronics (01-2017 - 11-2023)
IV - Methods: cloud cover by month
Cloud cover by month
Cloud cover the study area by month (01-2017 - 11-2023)
High proportion of clouds in January.
IV - Methods: algorithm
Water detection
The chosen algorithm: the Python package WaterDetect (Cordeiro, Martinez, and Peña-Luque (2021))
Advantages:
- automatic threshold for water detection (useful for temporal analysis)
- very few False Positive water pixels
- remove not pure water pixels (shores are excluded)
IV - Methods: effect of the algorithm
WaterDetect VS MNDWI VS AWEI
Example for the 2022-04-10 comparing WaterDetect and the MNDWI (Feyisa et al. (2014))
WaterDetect is spatially more precise.
IV - Methods: effect on the water mask
Implications of the choice of the water mask
Direct impacts of the water mask in the water quality parameters calculations.
IV - Methods: water quality from space
The water quality is linked to the water colour
The suspended and dissolved matters change the colour of water and thus its spectral signature.
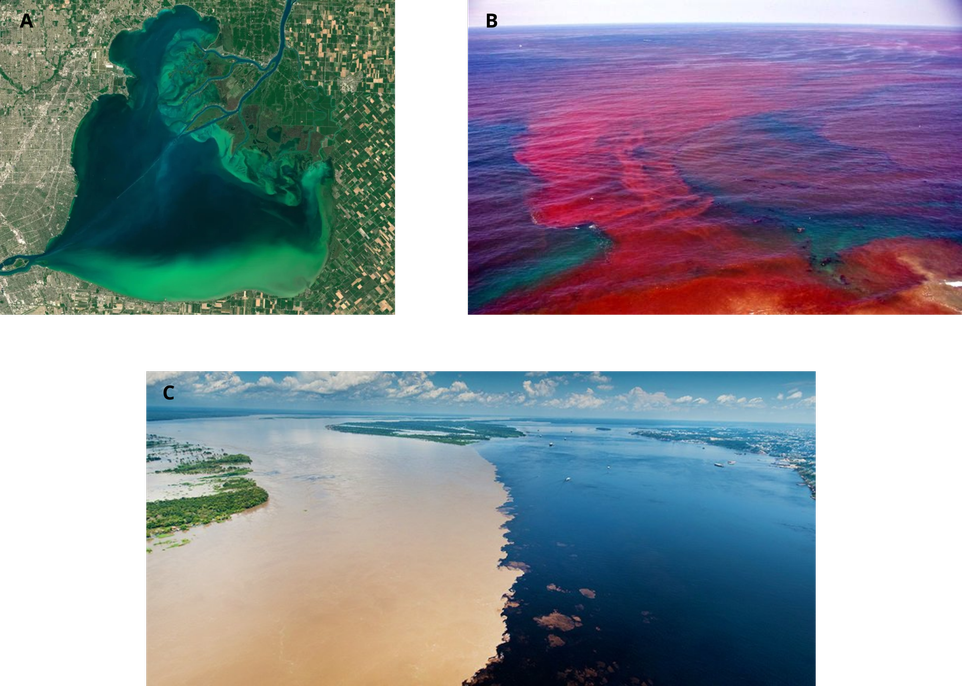

A) “Green waters” Algal bloom, B) “Red waters” Harmful algae bloom, C) Rio Negro - Amazon confluence
IV - Methods: signal inversion
Signal inversion of the Sentinel-2 reflectances to obtain water quality parameters
SPM: Suspended Particulate Matter
According to Nechad (Nechad, Ruddick, and Park (2010))
\[ spm = a \times \frac{Red}{(1 - \frac{Red}{c})} \]
with:
- Red: the reflectance in the Red band
- a: 610.94
- c: 0.2324
High concentrations of SPM may reflect high rates of erosion in the upstream watershed.
According to Dogliotti (Dogliotti et al. (2015))
"""Switching semi-analytical-algorithm computes turbidity from red and NIR band
following Dogliotti et al., 2015
:param water_mask: mask with the water pixels (value=1)
:param rho_red : surface Reflectances Red band [dl]
:param rho_nir: surface Reflectances NIR band [dl]
:return: turbidity in FNU
"""
limit_inf, limit_sup = 0.05, 0.07
a_low, c_low = 228.1, 0.1641
a_high, c_high = 3078.9, 0.2112
t_low = nechad(Red, a_low, c_low)
t_high = nechad(Nir2, a_high, c_high)
w = (Red - limit_inf) / (limit_sup - limit_inf)
t_mixing = (1 - w) * t_low + w * t_high
t_low[Red >= limit_sup] = t_high[Red >= limit_sup]
t_low[(Red >= limit_inf) & (Red < limit_sup)] = t_mixing[(Red >= limit_inf) & (Red < limit_sup)]
t_low[t_low > 4000] = 0
return t_lowwith:
- Red: the reflectance in the Red band
- Nir: the reflectance in the NIR band
High turbidity may reflect high rates of erosion in the upstream watershed or high algal productivity within the water column.
According to Gitelson and Kondratyev, 1991
\[ chl = 61.324 \times \frac{RedEdge1}{Red} - 37.94 \]
with:
- Red: the reflectance in the Red band
- RedEdge1: the reflectance in the Red edge 1 band
High concentrations of chlorophyll reflects high algal productivity and maybe high loads of nutrients.
CDOM: Colored dissolved organic matter is the optically measurable component of dissolved organic matter in water.
According to Brezonik (Brezonik et al. (2015))
\[ cdom = \exp(1.872 - 0.830 \times \log(\frac{Blue}{RedEdge2})) \]
High concentrations of CDOM may reflect high loads of dissolved organic matter from the watershed.
IV - Methods: let’s recap
The chain of treatments
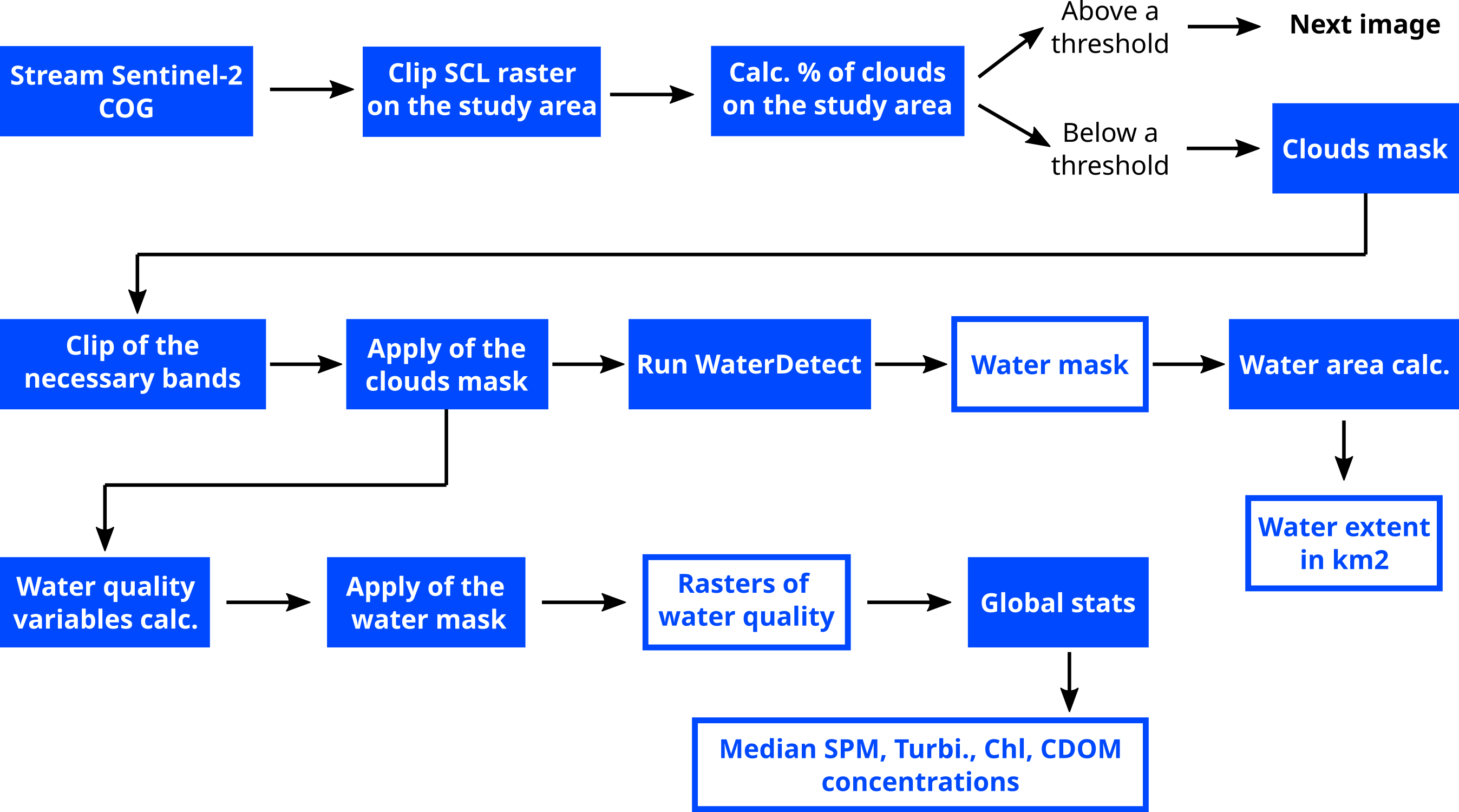
The global chain of treatments
V - Results: chronics of water extents
Water extents on the whole period
High intra-annual variations.
V - Results: water extents by year
Water extents by year
On average the extents were the highest in 2020.
Minimum values need to be manually checked!
V - Results: water extents by month
Water extents by month
Min extent → March - Max extent → August
V - Results: chronics of SPM
Chronics of SPM (2017 - 2023)
Median SPM concentrations by year
Less SPM in 2020.
Median SPM concentrations by month
Max SPM → June - Min SPM → December.
V - Results: chronics of turbidity
Chronics of turbidity (2017 - 2023)
Median turbidity by year
Less turbidity in 2020.
Median turbidity by month
Max turbidity → June - Min SPM → December.
V - Results: chronics of Chlorophyll
Chronics of chlorophyll (2017 - 2023)
Median chlorophyll concentrations by year
No clear trends for chlorophyll.
Median chlorophyll concentrations by month
Max chlorophyll → September - Min chlorophyll → December.
V - Results: chronics of CDOM
Chronics of CDOM (2017 - 2023)
CDOM median by year
No clear trends for CDOM
CDOM median by month
Two peaks for CDOM → June and October.
V - Results: correlations
Correlation between water extents and water quality parameters
What are the links between the water extents and the variations in terms of water quality?
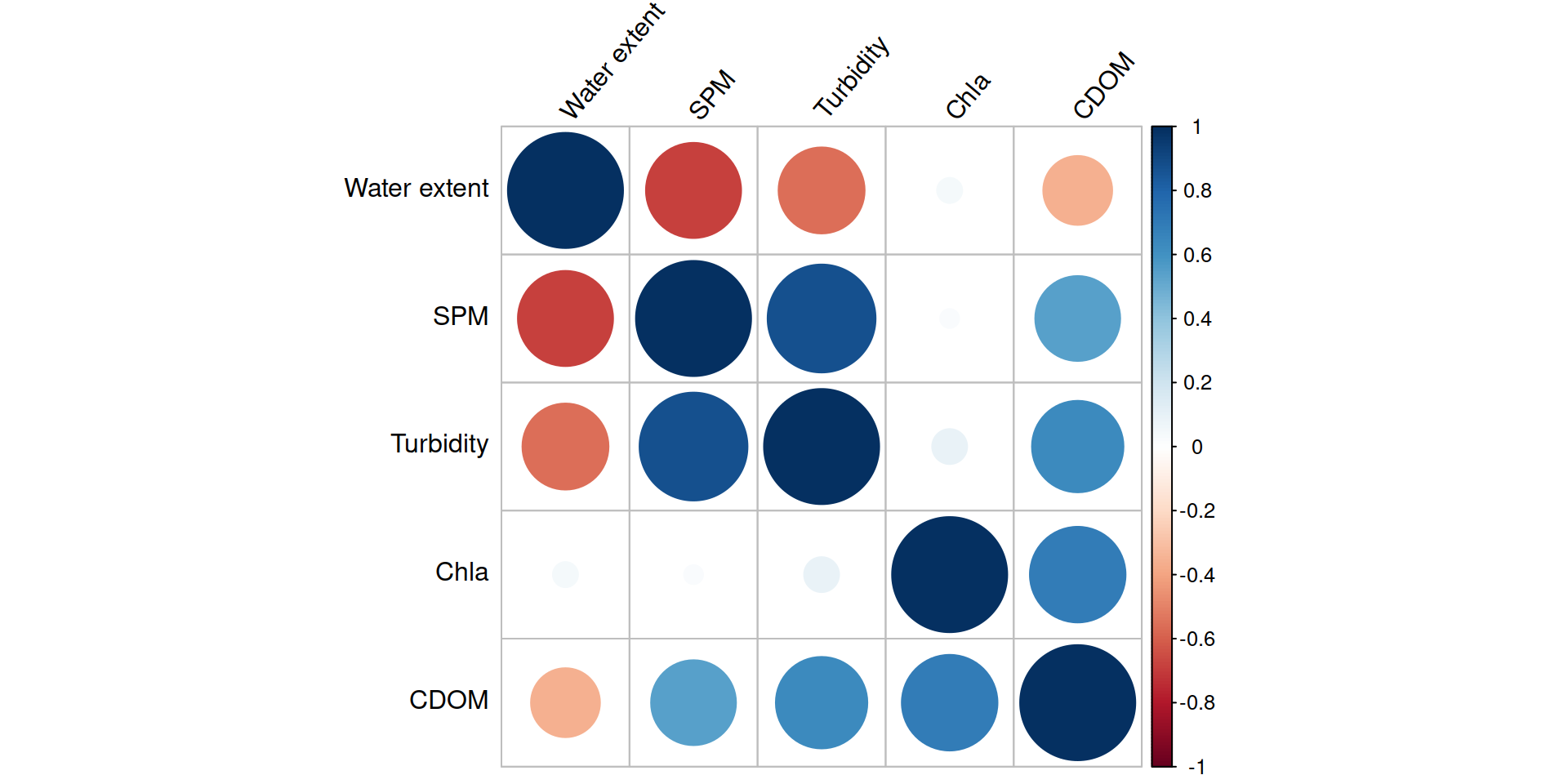
- Low water extents: large SPM, Turbidity and CDOM concentrations
- Large water extents: low SPM, Turbidity and CDOM concentrations
- Chlorophyll is not correlated to any other parameter
V - Results: water quality mapping
Spatio-temporal variations of the water quality
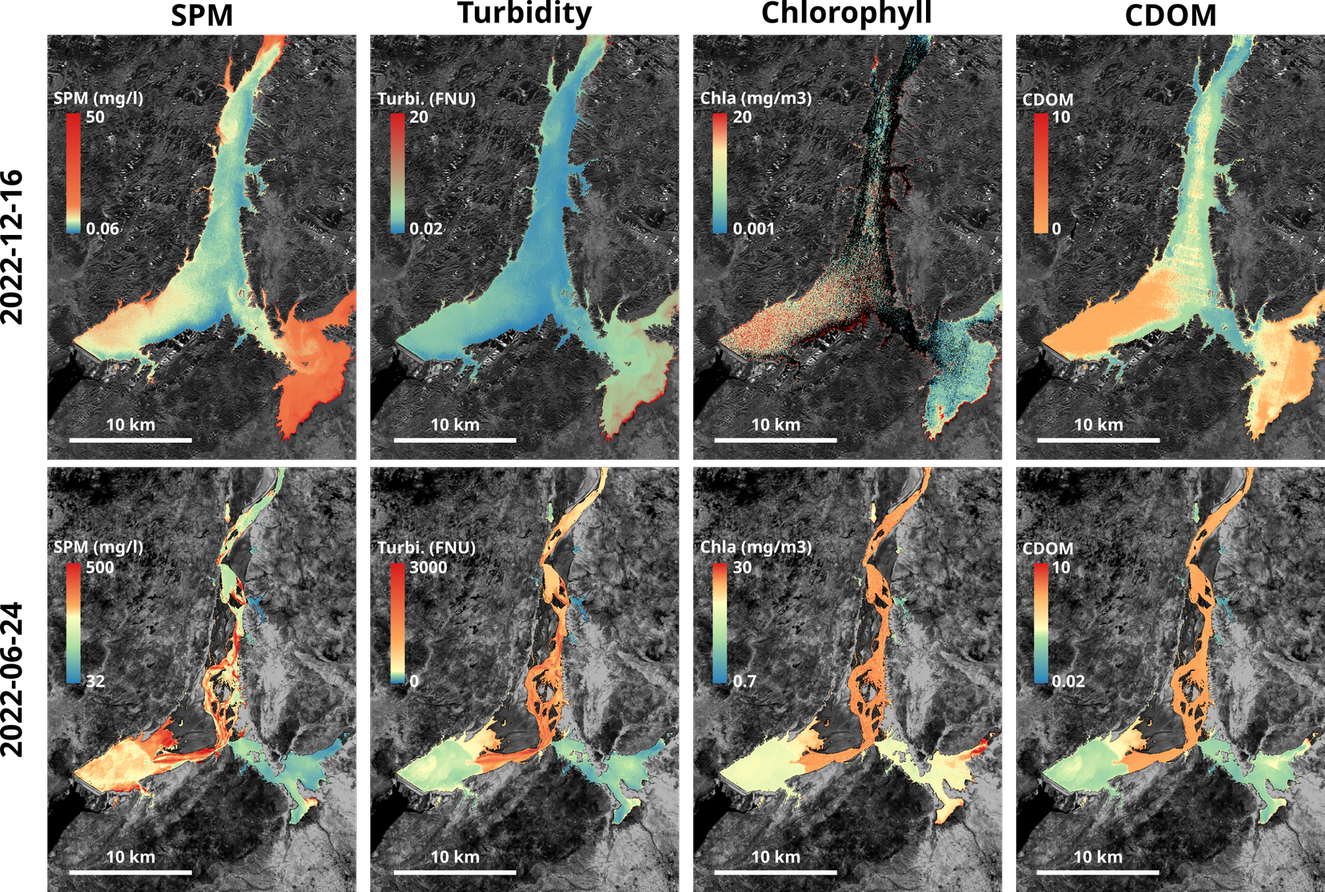
Water quality for June and December 2020
High intra-annual variability
V - Limits and perspectives
Limits
- In some cases the WaterDetect algorithm does not detect all the water
- Comparison with in-situ measurements
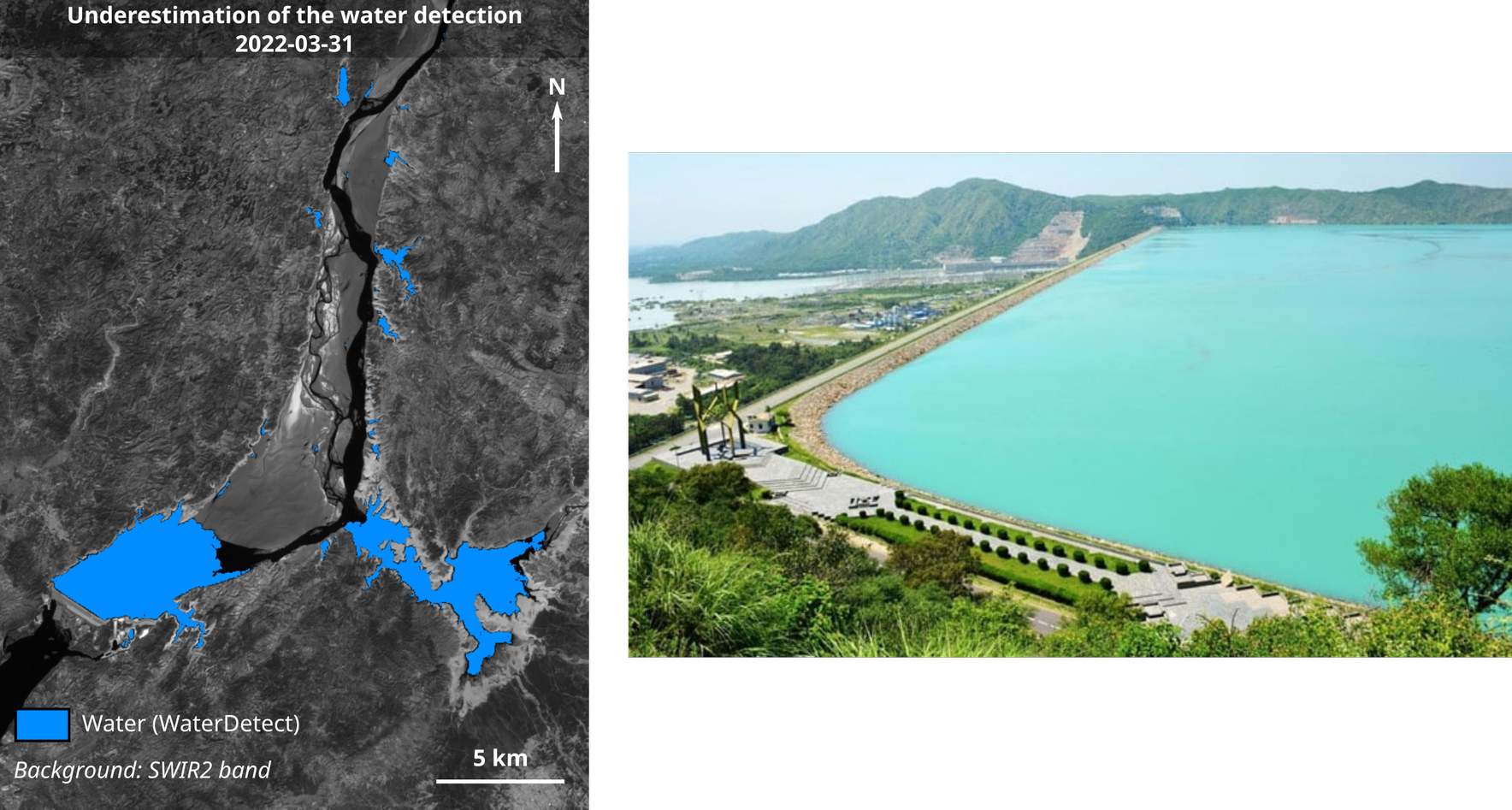

Under estimation of the WaterDetect algorithm and in-situ measurements
V - Limits and perspectives
Perspectives
Concerning the Tarbela reservoir monitoring
- Consolidate the results (check the water detection for different dates)
- Explore a longer chronics using the Landsat archives (water quality mapping issues?) (Maciel et al. (2023))
Concerning the upstream watershed
V - Conclusion
- we developed an automatic treatment chain to survey the Tarbela reservoir from Sentinel-2 images
- 158 Sentinel-2 images were treated from 2017-03-27 to 2023-11-16
- we highlighted trends in terms of water extents
- at the scale of one year: min extent in March and max extent in August
- at the scale of the period: largest extent in 2020 and smallest extent in 2018
- we highlighted trends in terms of water quality variations
- at the scale of one year:
- SPM and turbidity max in June
- SPM and turbidity min in December
- CDOM shows two peaks in the year in June and in October
- at the scale of the period:
- SPM and turbidity are lower in 2020
- chlorophyll and CDOM seem to be more stable through time
- at the scale of one year:
شکریہ
References

